Keywords: Adaptation analysis, climate change, transport networks, Argentina
This study was funded by the World Bank via Global Facility for Disaster Reduction and Recovery (GFDRR)
Transport systems in Argentina are severely affected by widespread flooding, resulting in major incidents where road failures. This study responded to the technical assistance sought by the World Bank to support the Government of Argentina to identify locations of vulnerabilities and risks in transport systems due to external shocks from natural hazards driven by climate change in the country.
What we did
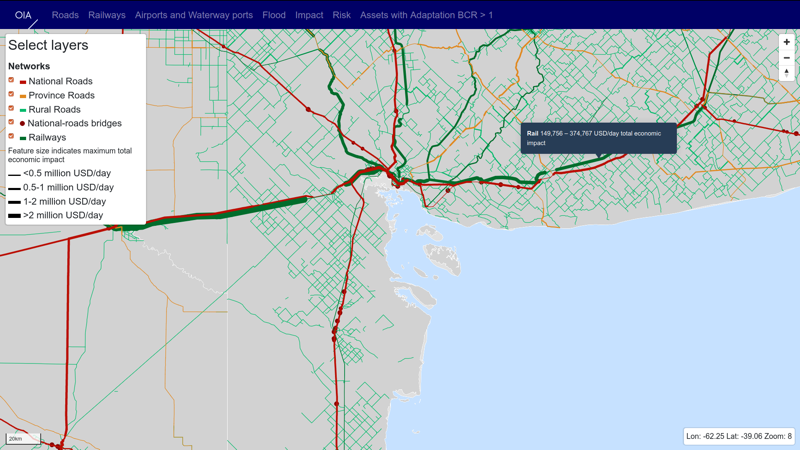
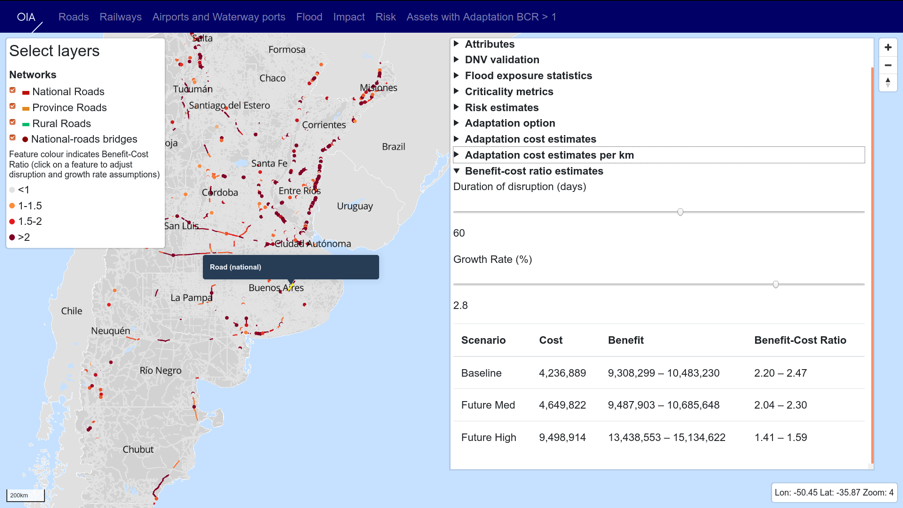
The scope of the analysis was to quantify criticality, vulnerability, risk and adaptation metrics for Argentina’s multi-modal networks of national, province and rural roads; bridges on national roads; national railways; major waterway ports; and major airports. This provided the rationale for prioritizing investments in the transport sector to reduce vulnerability and to create the basis for long term adaptation planning. By investigating transport risks in the context of climate-change driven extreme fluvial and pluvial flooding in the present and future, the analysis showed that several locations on Argentina’s road networks and national road bridges required investments to upgrade existing assets to higher climate resilient design standards. Though the costs of such investments could be high, the benefits of avoiding flood damages and disruption losses outweigh the investment costs for many assets, and the case for investing in climate resilience became stronger as the durations of disruptive impacts increased.
Results & insights
The study showed that Argentina’s transport sectors need to be prepared for increasingly extreme flooding exposures, which will be magnified in the future with increasing frequencies due to climate change.
Several locations on Argentina’s road networks and national-roads bridges require investments to upgrade existing assets to higher climate resilient design standards. Though the costs of such investments could be high for a large number of assets the benefits of avoiding flood damages and disruption losses outweigh the investment costs. The case for investing in climate resilience becomes stronger as the duration of disruptive impacts increases, which in turn means that investing in reducing the duration of disruption should be a priority of adaptation planners in Argentina.
Impact
The study created a unique web-based tool for data inquiry and detailed network-scale climate risks and adaptation outcomes, which was integrated into the systems being used by the Ministry of Transport in Argentina.
Project duration:
May 2018 – August 2019
Institutions:
Environmental Change Institute, University of Oxford
Related models and datasets:
- argentina-transport on GitHub
- Argentina Transport Risk Analysis – Documentation
- oi-risk-vis on GitHub
Oxford Team member Dr. Raghav Pant presenting Argentina project findings at the DMDU conference in Delft in November 2019. (Photo credit: Dr. Homero Paltan)






